

The bacterial plasma membrane is a lipid bi-layer membrane found within the cell wall.
The cell wall maintains bacteria shape and provides protection. It covers outside of the plasma membrane. The bacterial cell wall is a rigid barrier made of carbohydrate polymers and peptidoglycan proteins (different from the plant and fungal cell walls). Flagellum Tail-like structure assists in the movement Cell wall Pilus Hair-like structures help with cellular attachment and DNA transfer. The capsule helps the bacterium attach to surfaces. Capsule Some bacteria have a layer of carbohydrates that surrounds the cell wall called the capsule or glycocalyx. Most bacteria have a rigid cell wall made from carbohydrates and proteins called peptidoglycans. Cell wall Provides structure and protection from the outside environment. Cell membrane Also known as the plasma membrane that separates the cell from the outside environment. Cytoplasm Cellular fluid hosting all other cellular structures. Plasmid A small circular piece of DNA that is physically separated from chromosomal DNA. Cell Structure Functions Nucleoid A central region of the cell contains its DNA. Below is a breakdown of what you might find in a bacterial cell. While bacteria do not have membrane-bound organelles, they do have distinct cellular structures to survive. Diagram of a bacterium showing its cellular structures. The name, Prokaryote, came from Old Greek: pro- = before karyon = nut or kernel, referring to the cell nucleus suffix -otos, pl. Bacteria and archaea are two major branches of prokaryotes. Prokaryotic cells tend to be small, simple cells, measuring around 0.1-5 μm in diameter. Let’s do physical exams on bacteria to know more about them!īacteria are prokaryotes (pro-KAR-ee-ot-es), which means they have no nucleus or membrane-bound organelles (i.e., mitochondria or chloroplasts). The earth is estimated to hold at least 5 nonillion (5 followed by 30 zeros) bacteria, and much of the earth’s biomass is thought to be made up of bacteria.A milliliter of fresh water usually holds about one million bacterial cells. A gram of soil typically contains about 40 million bacterial cells.It requires 1000x magnification to see them well. The size comparison between our hair (~ 60 µm) and E. Bacteria usually measure a few micrometers (usually 1-1.5 µm) in length and exist together in communities of millions.The oldest known fossils (found in western Australia) are of cyanobacteria, dated 3.5 billion years old. Bacteria are thought to be the first living organisms on earth, about 4 billion years ago.A relatively small number of bacteria are parasites or pathogens that cause disease in animals and plants. Some types cause food spoilage and crop damage, but others are incredibly useful in producing fermented foods such as yogurt and soy sauce. Some bacteria live in the soil or on dead plant matter, where they play an essential role in cycling nutrients. Most bacteria in our body are harmless, and some are even helpful. Colored electron micrograph of Rod-shaped bacteria. A lot of these bacteria reside in our gut, called the microbiome.
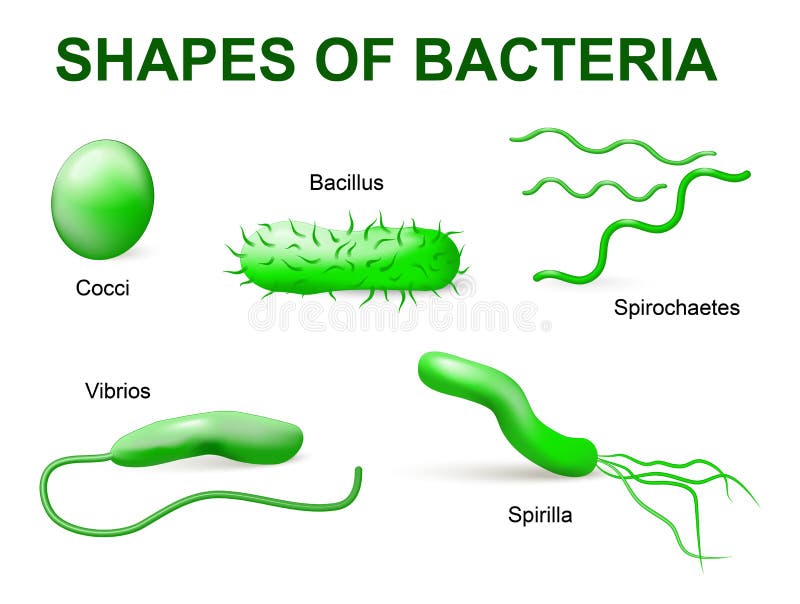
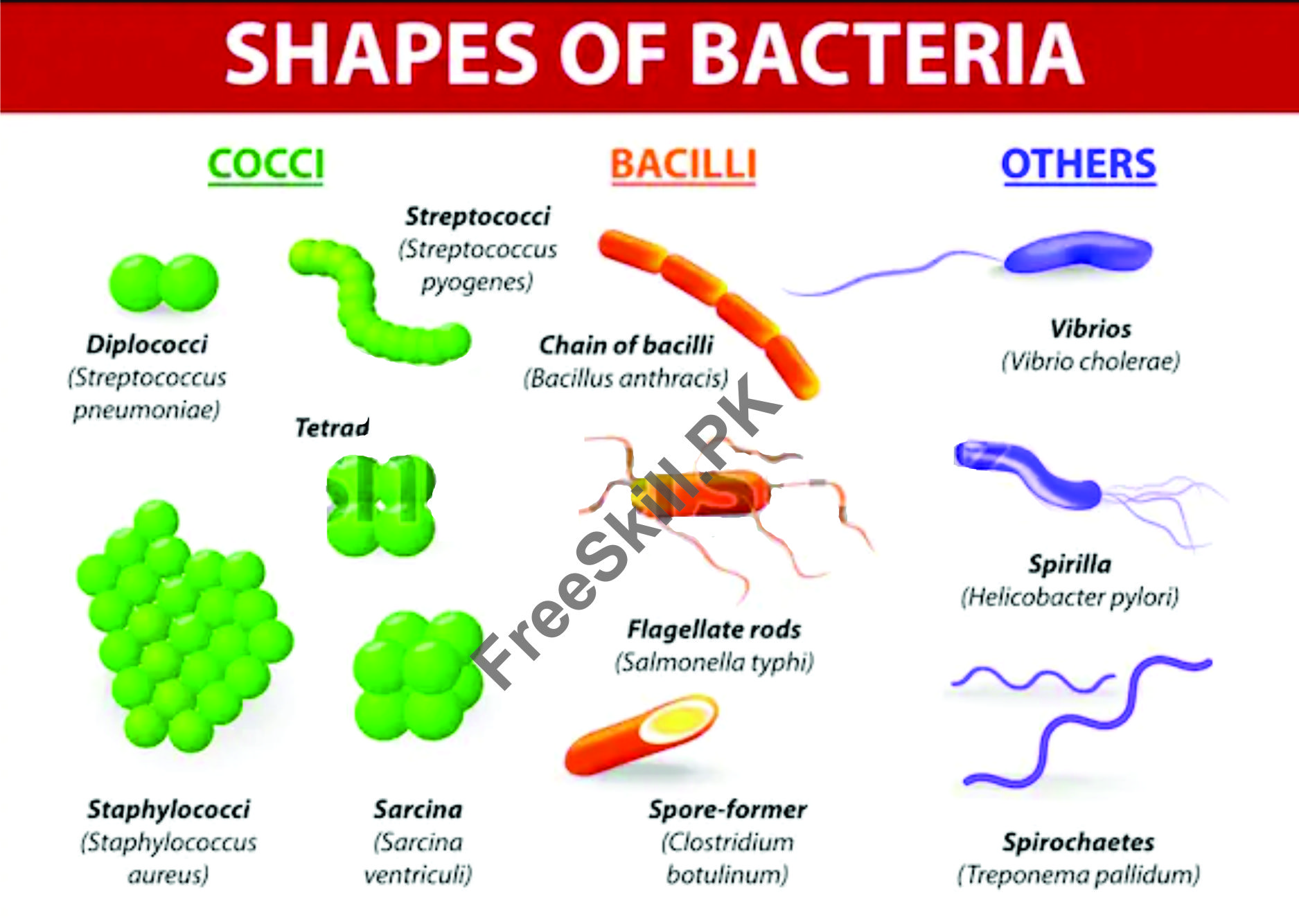
DIFFERENT TYPES OF BACTERIA SHAPES AND INFO FULL
The human body is full of bacteria, and in fact, is estimated to contain 10 times more bacterial cells than human cells in our body. Some live in or on other organisms, including plants and animals. Some species can live in extreme conditions of temperature and pressure. References What are bacteria? A quick overviewĮukaryotes and Prokaryotes – What are the Similarities, Differences, and Examplesīacteria are found almost everywhere on Earth – soil, rock, oceans, and even arctic ice.What are the differences between bacteria and archaea?.Frequently asked questions and answers (Q&A).Observing bacteria in a Petri dish or under a microscope Bad bacteria: pathogens and infectious diseases.What is life? Is bacterium a living thing?.Classification by ribosomal RNA sequences.Classification by the source of nutrients.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
